Architectural Maquettes: Crafting the Future of Design
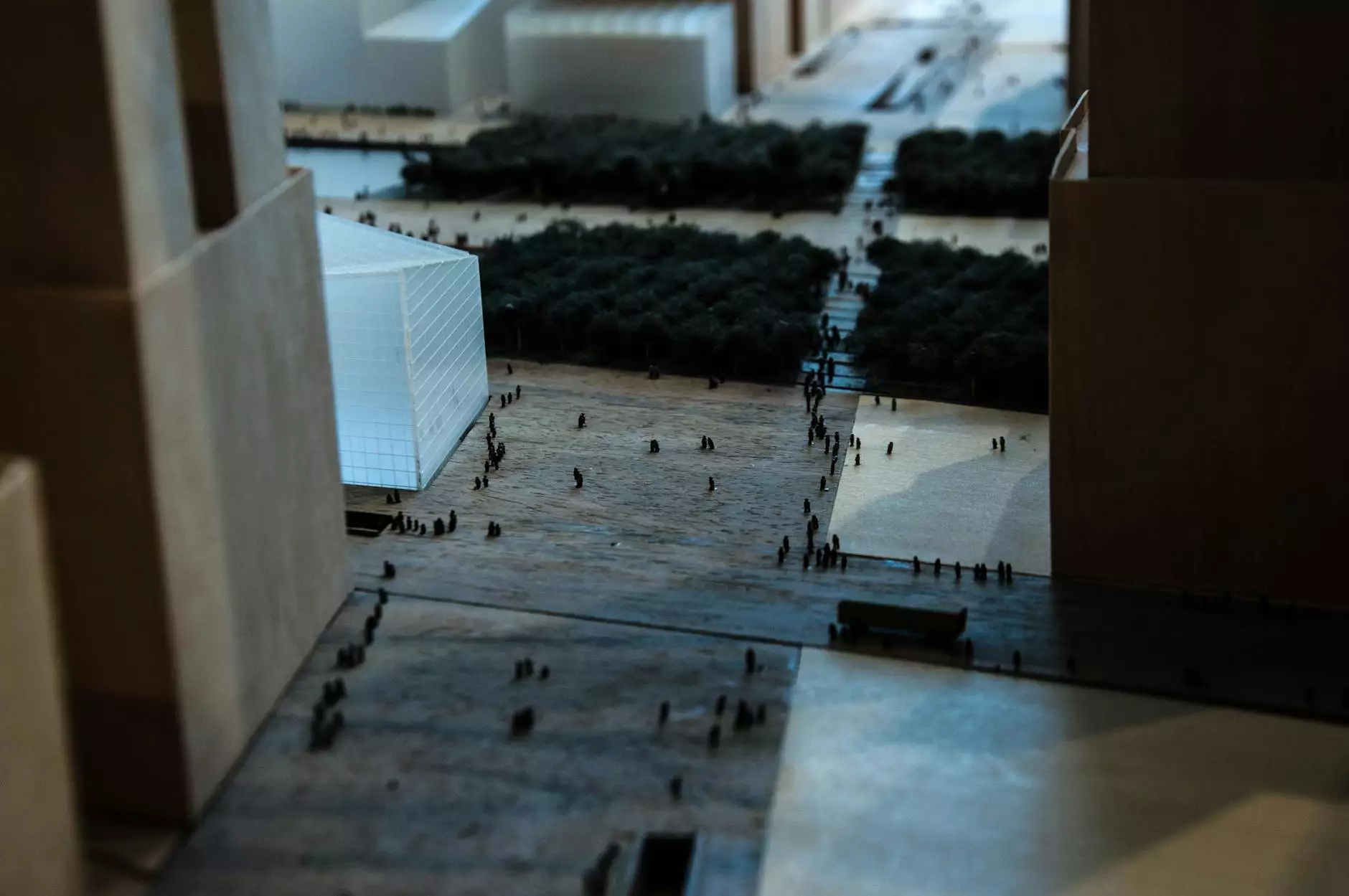

The realm of architecture extends beyond mere structures; it envelops innovation, art, and meticulous attention to detail. Among the various methods architects employ to visualize and communicate their ideas, architectural maquettes stand out as a powerful tool. These three-dimensional models not only represent a physical manifestation of creative concepts but also serve as vital instruments in the design and planning phases of architectural projects.
What are Architectural Maquettes?
Architectural maquettes are detailed scale models of structures that provide a tangible representation of an architect's vision. Traditionally constructed from a variety of materials including cardboard, wood, and plastics, these models allow architects to explore spatial relationships, materials, light, and proportions in a way that digital models cannot fully replicate.
The Importance of Architectural Maquettes in Design
The creation of architectural maquettes has several advantages that enhance both the design process and client communication. Here are some key benefits:
- Enhanced Visualization: Maquettes allow stakeholders to see and understand the physical scale and massing of a project before construction begins.
- Spatial Relationships: They help in visualizing spatial dynamics, allowing designers to assess how space interacts within the environment.
- Material Experimentation: Designers can explore color and texture by using various materials, giving clients a more comprehensive understanding of the finished project.
- Design Iteration: Physical models enable quick alterations; architects can manipulate and refine designs effortlessly, fostering creativity and spontaneity.
- Effective Communication: They serve as a universal language among clients, architects, and builders, reducing the chances of misunderstandings.
The Process of Creating Architectural Maquettes
The journey from concept to architectural maquettes involves several stages that demand creativity, precision, and attention to detail. Here’s a breakdown of the process:
1. Concept Development
The first stage begins with the architect’s conceptualization of the project. Sketches and drawings are created to lay the foundational idea, focusing on key elements like purpose, location, and overall design aesthetic.
2. Selection of Materials
Once the concept is clear, selecting appropriate materials for the maquette is crucial. Common materials include:
- Cardboard: Cost-effective and easy to work with, perfect for preliminary models.
- Wood: Provides a sturdy, natural aesthetic and is ideal for more refined models.
- Foam Board: Lightweight and versatile, excellent for detailed presentations.
- Plastic: Durable and allows for precision cutting, useful in intricate designs.
3. Building the Model
The construction phase involves careful cutting, measuring, and assembling the chosen materials. This stage requires the architect’s artisan skills to ensure that the maquette accurately reflects the intended design as closely as possible.
4. Detailing
Adding details such as textures, colors, and contextual elements like landscape and furniture transforms the maquette into a more comprehensive representation.
5. Presentation
The final step is presenting the architectural maquette to clients or stakeholders. This includes explaining the design rationale, material choices, and how the project intends to harmonize with its environment.
Types of Architectural Maquettes
Architectural maquettes can be classified into various types, each serving a distinct purpose:
- Presentation Models: Highly detailed and visually appealing, these models are used for showcasing projects to clients or for exhibits.
- Study Models: Often more abstract and less detailed, study models focus on exploring form and spatial relationships.
- Contextual Models: These incorporate the surrounding environment and show how the project fits within its context.
- Structural Models: Emphasizing engineering aspects, these models illustrate load-bearing elements and construction methods.
Innovations in Architectural Maquettes
As technology evolves, so do the techniques and tools available to architects. New innovations have begun to transform the creation and application of architectural maquettes:
1. 3D Printing
With advancements in 3D printing technology, architects can create highly detailed models quickly and efficiently. This technology allows for intricate designs that would be time-consuming to produce by hand.
2. Digital Fabrication
Tools such as laser cutters and CNC machines enable precise manufacturing of model components, ensuring high accuracy and repeatability.
3. Augmented Reality (AR) and Virtual Reality (VR)
Integrating AR and VR with architectural maquettes allows for immersive experiences. Clients can visualize how a space operates within its environment, viewing it from multiple perspectives and even simulating different times of day to see lighting effects.
Case Studies: Successful Use of Architectural Maquettes
To highlight the effectiveness of architectural maquettes, consider the following case studies:
1. The Guggenheim Museum Bilbao
When designing the Guggenheim Museum in Bilbao, architect Frank Gehry relied heavily on maquettes to explore complex forms and spatial relationships. The iteration process allowed him to refine ideas that ultimately resulted in a groundbreaking design.
2. The Sydney Opera House
Jørn Utzon used maquettes throughout the design process of the Sydney Opera House, allowing him to assess the structure's distinct sail-like roofs and their interaction with the harbor. The final maquettes proved crucial in communicating the project’s vision to stakeholders.
Conclusion
Architectural maquettes represent a bridge between imagination and reality in the field of architecture. They provide a platform for creativity while serving as essential tools for visualization, communication, and design development. As we continue to innovate and adapt to new technologies, the role of architectural maquettes will undoubtedly evolve, but their core significance will forever remain—helping architects and clients together in the journey of creating spaces that inspire and endure.